The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) have approved the use of a new superbug-busting faecal transplant that could not only improve the lives of hundreds of patients but save the NHS thousands of pounds as well.
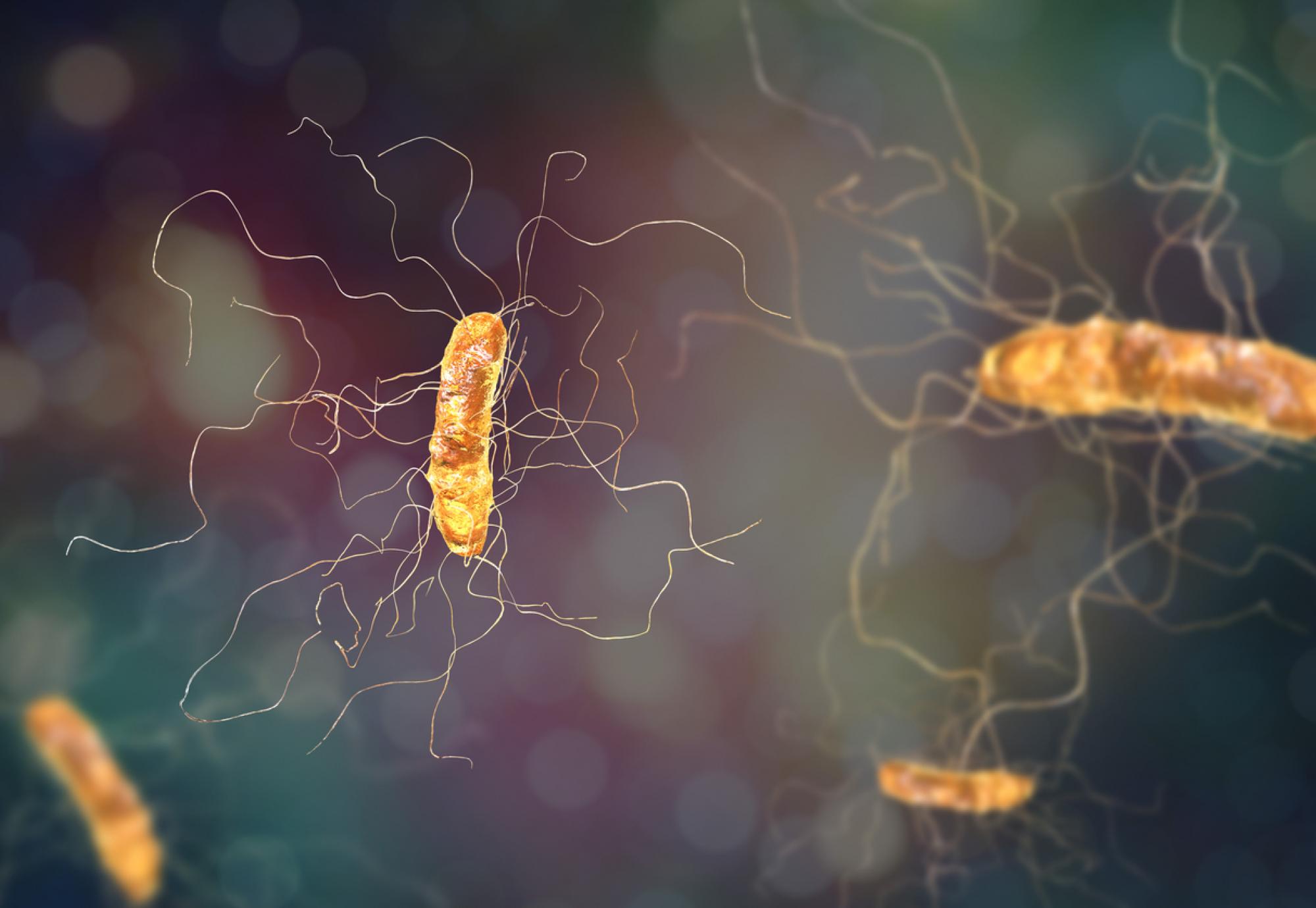
Clostridium difficile – also known as C. diff – is a bacterium that causes an onset of infection if there is a shift in the balance of bacteria in the bowels, ultimately leading to patients suffering from diarrhoea and general discomfort.
But now, following positive results from a series of clinical trials, those who have been unsuccessfully treated two or more times for C. diff will be offered a faecal microbiota transplant (FMT) – a treatment that involves transferring gut bacteria from a healthy person’s poo into the gut of the patient in order to re-establish a healthy population of bacteria.
Evidence from clinical trials showed that a greater proportion of C. diff infections were cleared up using FMT than with a standard course of antibiotics in four of the five randomised trials. The studies also indicated that, whilst effectiveness can fluctuate based on how the treatment is delivered, FMT could resolve up to 94% of C. diff infections.
Furthermore, not only does FMT have the potential to improve patient health outcomes, but it could also save the NHS thousands of pounds every single year, with price modelling showing that it is cheaper than almost all antibiotic treatments.
When delivered via a colonoscopy, FMT saves the NHS £769 compared to vancomycin taper pulse, whilst saving £8,297 compared to vancomycin if delivered via an oral capsule.
Mark Chapman, interim director of Medical Technology at NICE, said: “There is currently a need for an effective treatment of C. diff in people who have had two or more rounds of antibiotics.
“Our committee’s recommendation of this innovative treatment will provide another tool for health professionals to use in the fight against this infection, while at the same time balancing the need to offer the best care with value for money.
“Use of this treatment will also help reduce the reliance on antibiotics and in turn reduce the chances of antimicrobial resistance, which supports NICE’s guidance on good antimicrobial stewardship.”
Donor bacteria can be delivered directly to the stomach via a tube inserted in the nose, or alternatively, clinicians can give the patient a pill to swallow, delivering the bacteria straight to the colon.
NICE have warned that FMT must be developed in accordance with the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency’s guidance and that a strict donor screening programme should be established to ascertain the risk factors pertaining to transmissible diseases.
More information on the new treatment is available here.